
The Basics
If you don’t already have a points system and aren’t sure where to start, we suggest you start with one of our preset points systems (Logarithmic, Square Root, Linear):

Take a look at each of them and see what you think of the sample points structure on the right.
Fixed
The “Fixed” option gives you some customization with a simple interface:
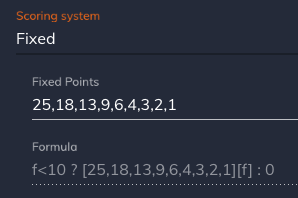
In the above example points will be attributed:
- 1st place: 25 points,
- 2nd place: 18 points,
- 3rd place: 13 points,
- etc.
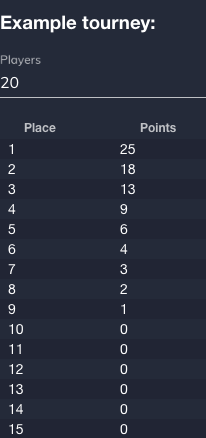
You can change the comma separated list of Fixed Points and the point payouts will change. You can always enter a number of players for an example tournament on the right and see if the point payouts are as you expected:
Custom Formulas
But the option we really want to talk about today is the “Custom” option where you can create your own points formula.

The image above shows the different variables available to you to use in your formulas.
Some of these are apply to the tournament as a whole:
- p = number of players
- b = buy-in
- z = prizepool
and some of them apply to the individual player:
- f = finish position
- c = total cost (buy-in + rebuys + addon)
- k = knockouts
Examples
Linear
If you select the “Linear” preset you can see the formula that is used here:
p-f+1
So if a player finishes 5th out of 30 players they would be given 26 points (30 – 5 + 1)
Fixed
We can see an example that the “Fixed” formula below:
f<10 ? [25,18,13,9,6,4,3,2,1][f] : 0
This looks complex but it is really just saying:
If the player finishes in better than 10th place:
Award points from this list [25,18,13,9,6,4,3,2,1] , if f=3 give me the 3rd, if f=5 give me the 5th, etc.
Otherwise, award 0 points
Linear with a bonus for winner
What if we want to use a “Linear” formula but give a winner’s bonus of 5 points?
In this case we can use a conditional expression:
X ? Y : Z
Which can be read as “If X then Y else Z”
So for our example, it would be:
p-f+1+(f==1 ? 5 : 0)
So this is a standard linear point system and then you add the bonus “if Finish Position == 1 then 5 bonus points else 0 bonus points”
Note: Always use the double equals sign “==” to compare if two values are equal
Fixed points for top 3 and participation point for everyone else
In this example we will give points as follows:
- 1st place: 10 points
- 2nd place: 7 points
- 3rd place: 4 points
- All others: 1 point
So here we can use modify slightly the fixed function:
f<4 ? [10,7,4][f] : 1
Which could read as: “If player’s finish is better than 4th place give them 10,7, or 4 points respectively, otherwise give them one point”
Just about any point system can be modeled with a custom formula. Give it a shot and let us know if you get stuck, we’ll be happy to help you find the formula that works for your system: support@blindvalet.com
Reference
Operators
| Operator | Name | Syntax | Associativity | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
+ |
Add | x + y |
Left to right | 4 + 5 |
9 |
- |
Subtract | x - y |
Left to right | 7 - 3 |
4 |
* |
Multiply | x * y |
Left to right | 2 * 3 |
6 |
/ |
Divide | x / y |
Left to right | 6 / 2 |
3 |
%, mod |
Modulus | x % y |
Left to right | 8 % 3 |
2 |
^ |
Power | x ^ y |
Right to left | 2 ^ 3 |
8 |
! |
Factorial | y! |
Left to right | 5! |
120 |
? : |
Conditional expression | x ? y : z |
Right to left | 15 > 100 ? 1 : -1 |
-1 |
: |
Range | x : y |
Right to left | 1:4 |
[1,2,3,4] |
== |
Equal | x == y |
Left to right | 2 == 4 - 2 |
true |
!= |
Unequal | x != y |
Left to right | 2 != 3 |
true |
< |
Smaller | x < y |
Left to right | 2 < 3 |
true |
> |
Larger | x > y |
Left to right | 2 > 3 |
false |
<= |
Smallereq | x <= y |
Left to right | 4 <= 3 |
false |
>= |
Largereq | x >= y |
Left to right | 2 + 4 >= 6 |
true |
Constants
| Constant | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
e, E |
Euler’s number, the base of the natural logarithm. | 2.718281828459045 |
LN2 |
Returns the natural logarithm of 2. | 0.6931471805599453 |
LN10 |
Returns the natural logarithm of 10. | 2.302585092994046 |
LOG2E |
Returns the base-2 logarithm of E. | 1.4426950408889634 |
LOG10E |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of E. | 0.4342944819032518 |
NaN |
Not a number. | NaN |
null |
Value null. | null |
phi |
Phi is the golden ratio. Two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Phi is defined as (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2 |
1.618033988749895 |
pi, PI |
The number pi is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. | 3.141592653589793 |
SQRT1_2 |
Returns the square root of 1/2. | 0.7071067811865476 |
SQRT2 |
Returns the square root of 2. | 1.4142135623730951 |
tau |
Tau is the ratio constant of a circle’s circumference to radius, equal to 2 * pi. |
6.283185307179586 |
Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | Calculate the absolute value of a number. |
| cbrt(x [, allRoots]) | Calculate the cubic root of a value. |
| ceil(x) | Round a value towards plus infinity If x is complex, both real and imaginary part are rounded towards plus infinity. |
| cube(x) | Compute the cube of a value, x * x * x. |
| exp(x) | Calculate the exponent of a value. |
| expm1(x) | Calculate the value of subtracting 1 from the exponential value. |
| fix(x) | Round a value towards zero. |
| floor(x) | Round a value towards minus infinity. |
| log(x [, base]) | Calculate the logarithm of a value. |
| log10(x) | Calculate the 10-base logarithm of a value. |
| log1p(x) | Calculate the logarithm of a value+1. |
| log2(x) | Calculate the 2-base of a value. |
| mod(x, y) | Calculates the modulus, the remainder of an integer division. |
| nthRoot(a) | Calculate the nth root of a value. |
| nthRoots(x) | Calculate the nth roots of a value. |
| pow(x, y) | Calculates the power of x to y, x ^ y. |
| round(x [, n]) | Round a value towards the nearest integer. |
| sign(x) | Compute the sign of a value. |
| sqrt(x) | Calculate the square root of a value. |
| square(x) | Compute the square of a value, x * x. |
| and(x, y) | Logical and. |
| not(x) | Logical not. |
| or(x, y) | Logical or. |
| xor(x, y) | Logical xor. |
| random([min, max]) | Return a random number larger or equal to min and smaller than max using a uniform distribution. |
| randomInt([min, max]) | Return a random integer number larger or equal to min and smaller than max using a uniform distribution. |
| mad(a, b, c, …) | Compute the median absolute deviation of a list with values. |
| max(a, b, c, …) | Compute the maximum value of a list with values. |
| mean(a, b, c, …) | Compute the mean value of a list with values. |
| median(a, b, c, …) | Compute the median of a list with values. |
| min(a, b, c, …) | Compute the maximum value of a list of values. |
| mode(a, b, c, …) | Computes the mode of a set of numbers or a list with values(numbers or characters). |
| prod(a, b, c, …) | Compute the product of a list with values. |
| std(a, b, c, …) | Compute the standard deviation of a list with values. |
| sum(a, b, c, …) | Compute the sum of a list with values. |
| var(a, b, c, …) | Compute the variance of a list with values. |
| acos(x) | Calculate the inverse cosine of a value. |
| acosh(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic arccos of a value, defined as acosh(x) = ln(sqrt(x^2 - 1) + x). |
| acot(x) | Calculate the inverse cotangent of a value, defined as acot(x) = atan(1/x). |
| acoth(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic arccotangent of a value, defined as acoth(x) = atanh(1/x) = (ln((x+1)/x) + ln(x/(x-1))) / 2. |
| acsc(x) | Calculate the inverse cosecant of a value, defined as acsc(x) = asin(1/x). |
| acsch(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic arccosecant of a value, defined as acsch(x) = asinh(1/x) = ln(1/x + sqrt(1/x^2 + 1)). |
| asec(x) | Calculate the inverse secant of a value. |
| asech(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic arcsecant of a value, defined as asech(x) = acosh(1/x) = ln(sqrt(1/x^2 - 1) + 1/x). |
| asin(x) | Calculate the inverse sine of a value. |
| asinh(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic arcsine of a value, defined as asinh(x) = ln(x + sqrt(x^2 + 1)). |
| atan(x) | Calculate the inverse tangent of a value. |
| atan2(y, x) | Calculate the inverse tangent function with two arguments, y/x. |
| atanh(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic arctangent of a value, defined as atanh(x) = ln((1 + x)/(1 - x)) / 2. |
| cos(x) | Calculate the cosine of a value. |
| cosh(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic cosine of a value, defined as cosh(x) = 1/2 * (exp(x) + exp(-x)). |
| cot(x) | Calculate the cotangent of a value. |
| coth(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic cotangent of a value, defined as coth(x) = 1 / tanh(x). |
| csc(x) | Calculate the cosecant of a value, defined as csc(x) = 1/sin(x). |
| csch(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic cosecant of a value, defined as csch(x) = 1 / sinh(x). |
| sec(x) | Calculate the secant of a value, defined as sec(x) = 1/cos(x). |
| sech(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic secant of a value, defined as sech(x) = 1 / cosh(x). |
| sin(x) | Calculate the sine of a value. |
| sinh(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic sine of a value, defined as sinh(x) = 1/2 * (exp(x) - exp(-x)). |
| tan(x) | Calculate the tangent of a value. |
| tanh(x) | Calculate the hyperbolic tangent of a value, defined as tanh(x) = (exp(2 * x) - 1) / (exp(2 * x) + 1). |
